Editor’s Guide: Picking operation refers to the process that the warehouse operator picks the designated goods from the warehouse after receiving the picking task, and the actual picking operation occupies a high proportion in the whole warehouse operation. This paper only shares the process of operation and product design, and does not involve related strategic logic such as location allocation and path planning.

Logically speaking, the selection in the warehouse is mainly divided into two modes: sorting while picking and sorting first; The sorting process can be subdivided into fruit picking sorting and sowing sorting. The types of orders targeted by these three methods are also different.
Pick while sorting: As the name implies, it means picking goods for employees directly according to the order, and the picking process is directly a sorting process. Mainly for orders with multiple products and multiple pieces, and the goods required for each order are very different.
Picking first and then sorting: it is to split the general picking and sorting into two links. General picking: picking all the goods needed in multiple orders from the warehouse (usually the general picking list after wave summary); Sorting: sorting one by one according to the outbound order. It is suitable for orders with different SKU and quantity of goods in single item, multiple items and multiple items.
The operation instructions for fruit picking and sowing will be expanded in detail in the following paragraphs.
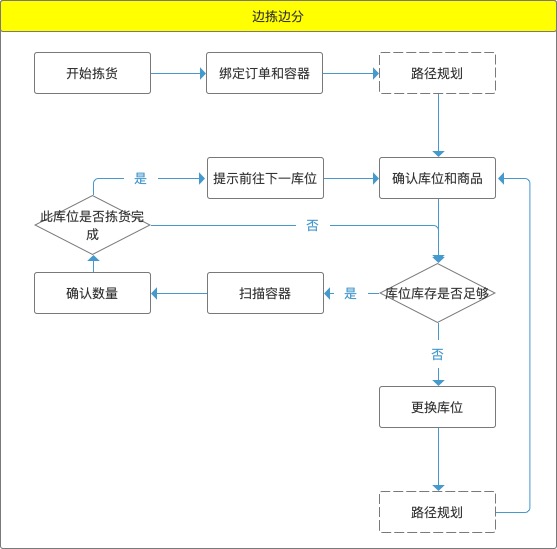
The above figure shows the personnel and system operation in the process of picking and dividing by flow chart.
Picking is the collection of picking tasks. Usually, the picking tasks in the warehouse are collected in the dimension of wave orders, that is, a picking task contains multiple orders. After receiving the task, before picking, the user needs to bind the container and the order in advance (the container code is attached to the container). After binding, the system will inform the user that N pieces of Y goods need to be picked and put into M containers in the subsequent picking process. In general practice, after binding, the operator will directly place the order in this container (there are also documents directly associated with equipment in the design, and paper documents are not needed).

Path planning is that the system outputs the shortest route according to the location of the required goods in the required order, combined with the route in the warehouse. This is the logic of the system, and the user is actually unconscious. After the planning is completed, the system outputs the first picking location to the user. According to the guidance, the user will pick the location here. In order to prevent users from making mistakes (because there are many warehouses and similar goods), it is suggested that before picking, the system requires users to confirm the goods that have arrived at the warehouse and will be picked by scanning the code (or combining with other hardware equipment). After confirmation, the user selects the corresponding number of commodities for each container according to the system prompt order, and confirms to scan the containers in the system and enter the number of selected commodities.
After a location finishes picking all the goods required by the order, the system will prompt the next location and the goods to be picked. This picking list will not be finished until all the goods are picked.
It is inevitable that there will be inventory differences in the warehouse. In the process of picking goods, it is embarrassing to find that there is insufficient inventory after going to the picking warehouse. Therefore, in the process of picking goods, it is necessary to support the reporting of abnormal inventory and secondary path planning. That is, after finding that the current location is out of stock, the system will be triggered by reporting to re-acquire the location with inventory and calculate the route.
In this case, the inventory of the current location will be frozen abnormally, and it is necessary for the exception handler to manually intervene the inventory after confirming the actual situation of the inventory.
In extreme cases (for example, there is really no goods in the warehouse), then this document needs to be reported manually and contacted with the demander (or customer) to confirm whether it is a partial delivery or a return.
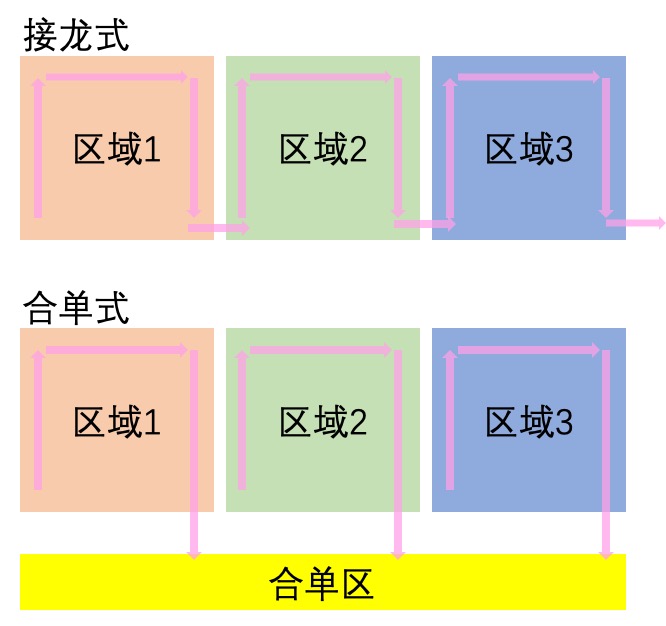
It is worth mentioning that for some warehouses with large storage capacity or managed by sub-storage areas, if an order is picked by a picker from beginning to end, it will lead to too many invalid paths and reduced efficiency due to unfamiliarity with the whole storage area.
There are usually two ways to deal with this situation:
- Through the way of solitaire, the task is segmented by many people from beginning to end until the picking is completed. After picking in area 1 is completed, the personnel will place the pickup truck in the handover area and complete the task in stages, and the picker in area 2 will continue to receive the task to pick the goods in the current area and continue the handover in the future.
- By splitting the task list in the warehouse (the most direct way is to split it according to the warehouse area to which the goods belong and the scope of the warehouse area to which the personnel are responsible), each person is only responsible for picking the goods in this area, and the picked containers are sent to the system to specify the partition position (the system will specify the same partition position for the regional picking tasks with the same order split), and the reviewer will check and pack the goods after the whole single picking is completed.
Picking while sorting is accurate for the confirmation and control of picking process, which requires users to confirm the location, goods, containers and picking quantity, and the operation accuracy is high. Suitable for picking with complex order structure. The disadvantage is that the cumbersome process has a certain impact on the operation efficiency. Therefore, for wave orders with simple order structure, the method of picking first and then sorting is usually used.
Total picking, also called total picking, refers to picking all the goods needed in the wave picking list from the warehouse first, and does not distinguish or operate the orders to which the specific goods belong during the picking process. For orders with simple order structure and large overall quantity, batch operation is beneficial to improve efficiency.
Taking platform sales as an example, it can be said that 20% of the goods account for 80% of the sales (explosive products), especially for activities and gift boxes, and this trend is more obvious. Therefore, the existence of this picking method can greatly improve the overall efficiency.
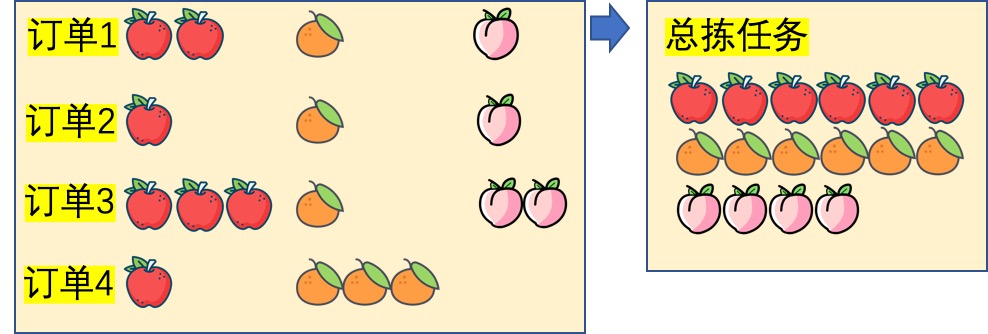
The operation and flow of the total picking process can be said to be the same as picking while dividing, and all of them are picking at the corresponding location according to the guidance of the system. The difference lies in:
- The selected goods are the goods needed by the whole wave order.
- There is no need to bind containers and orders, only need to associate containers with the current general picking list, which can be used to find the corresponding goods when sorting.
Therefore, this paragraph will not repeat the process decomposition.
The relationship between general picking and sorting:
In addition, the process of total picking and sorting is not strongly related, and it is not necessary to always pick before sorting. When designing a warehouse, a special sorting platform can be set for thermal goods (which can be understood as a hot picking location). For hot goods, besides the conventional location, this location also has inventory for a long time and triggers replenishment tasks according to the strategy. After receiving the sorting task, the sorter can directly operate the sorting at the sorting table, but there is no direct preorder general sorting operation.
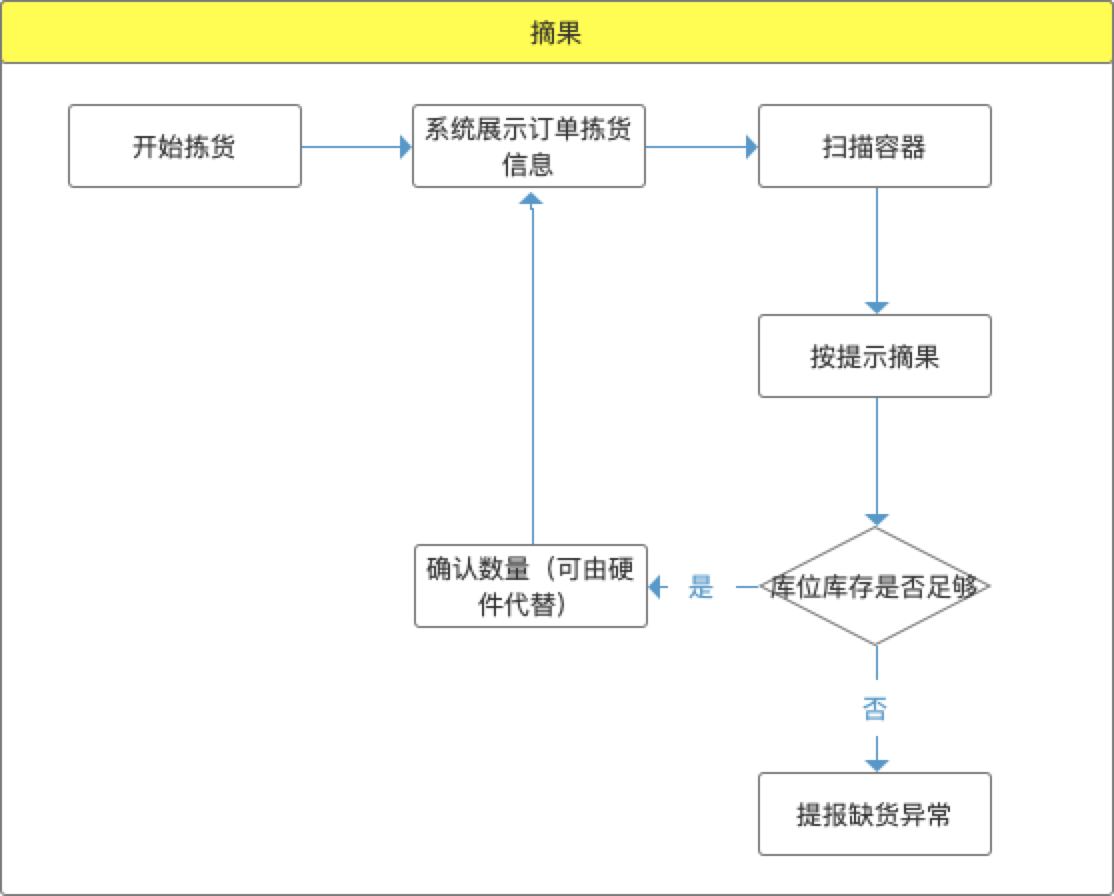
Fruit picking refers to picking out the goods one by one from the containers that are always picked according to the goods required by the order and placing them in the order container. Just like picking fruit from a fruit tree. Schematic diagram of fruit picking process:
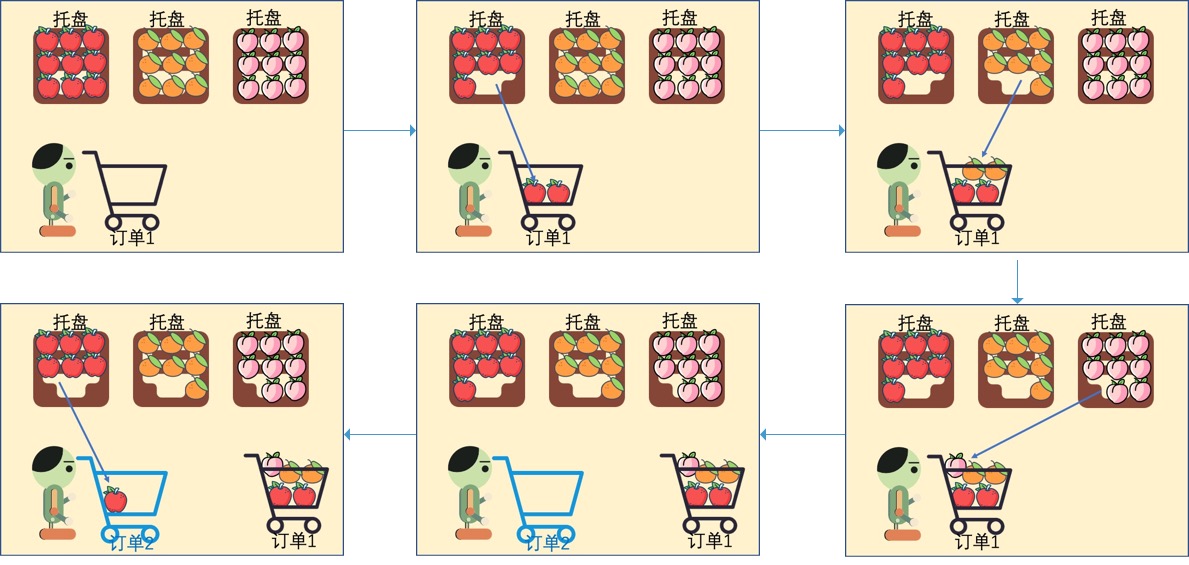
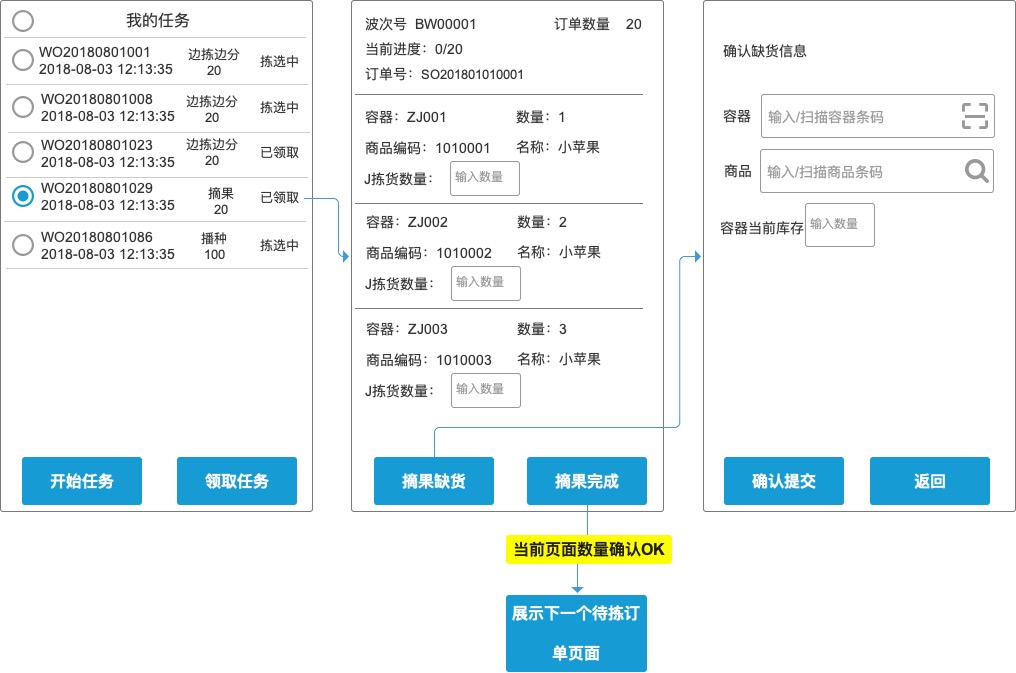
After picking fruits and picking goods, users actually sort each order. For the picking order displayed by the system, the user scans the container to associate this order. According to the demand information prompted by the system, a specified number of goods are selected from different general picking containers and placed in the containers. After picking is completed, submit the confirmed quantity and enter the picking of the next order.
Fruit picking and sorting are usually aimed at wave orders with the same SKU range and different user demand quantity. In order to improve the accuracy and efficiency of picking, the technology of electronic tag and pick to light can be combined to visually remind the picker of the quantity to be picked for this order. Reduce the interaction between users and the system.
Simplified system flow design:
Sowing is to operate the general picking tray, and the user distributes one commodity separately according to the goods needed in each order. It’s like a farmer’s uncle sowing seeds. Schematic diagram of seeding process:
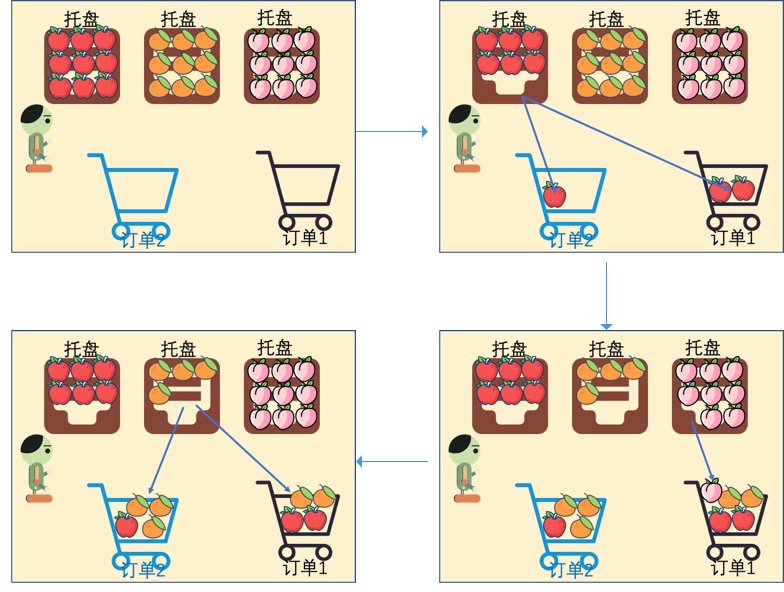
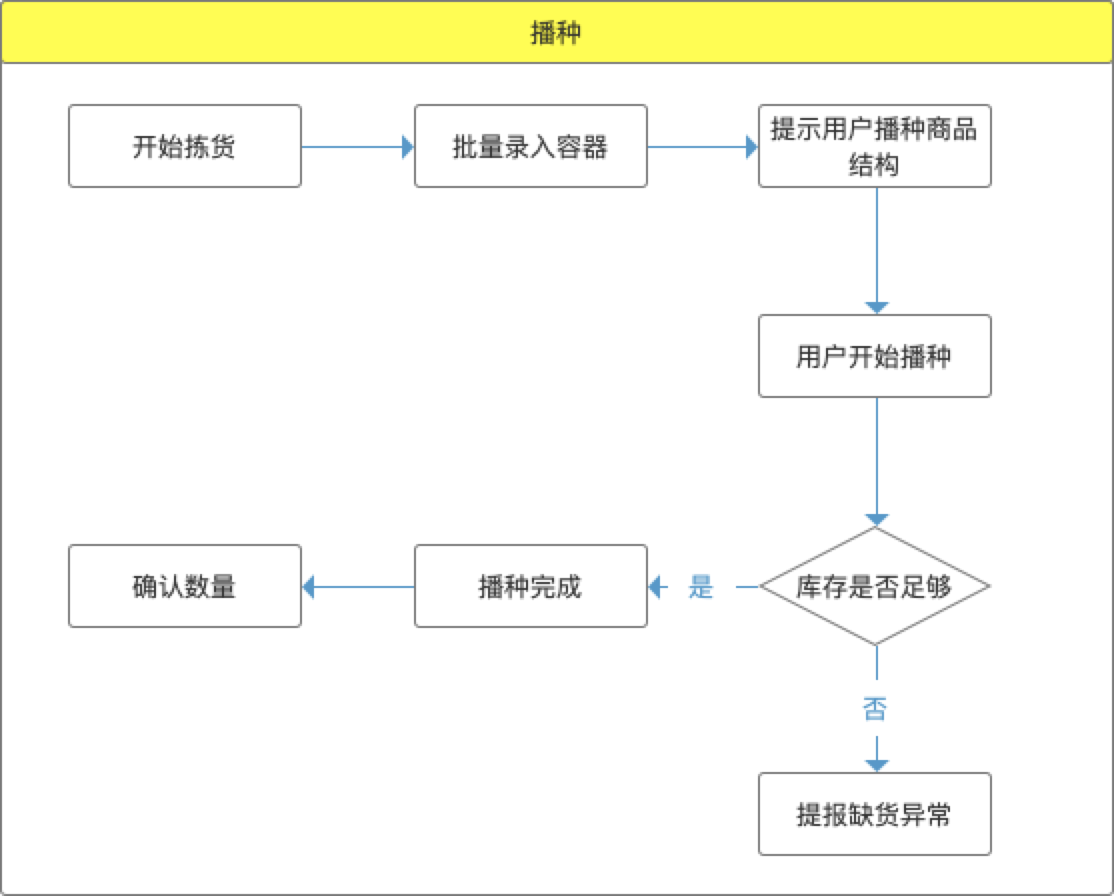
Although the goods in Order 1 and Order 2 are different in the above illustration, in most cases, the warehouse is mainly aimed at the same order structure. When the sowing and sorting method is adopted, this mode can almost become "brainless operation". The following flow chart is aimed at the mode of process design when the order structure is completely consistent.
After the operation is started, the user enters the container in batches according to the order quantity, and the system automatically matches the order with the container (for subsequent review). If the order is pre-typed, the user can directly place the order in the container, and the system does not need to bind the container operation. However, if the documents are lost on the way, they will be pitted, so there are still risks. After the container is entered, the system prompts the user to place the ordered goods (the same). After completion, confirm the quantity of goods in the system.
Simplified system flow design:
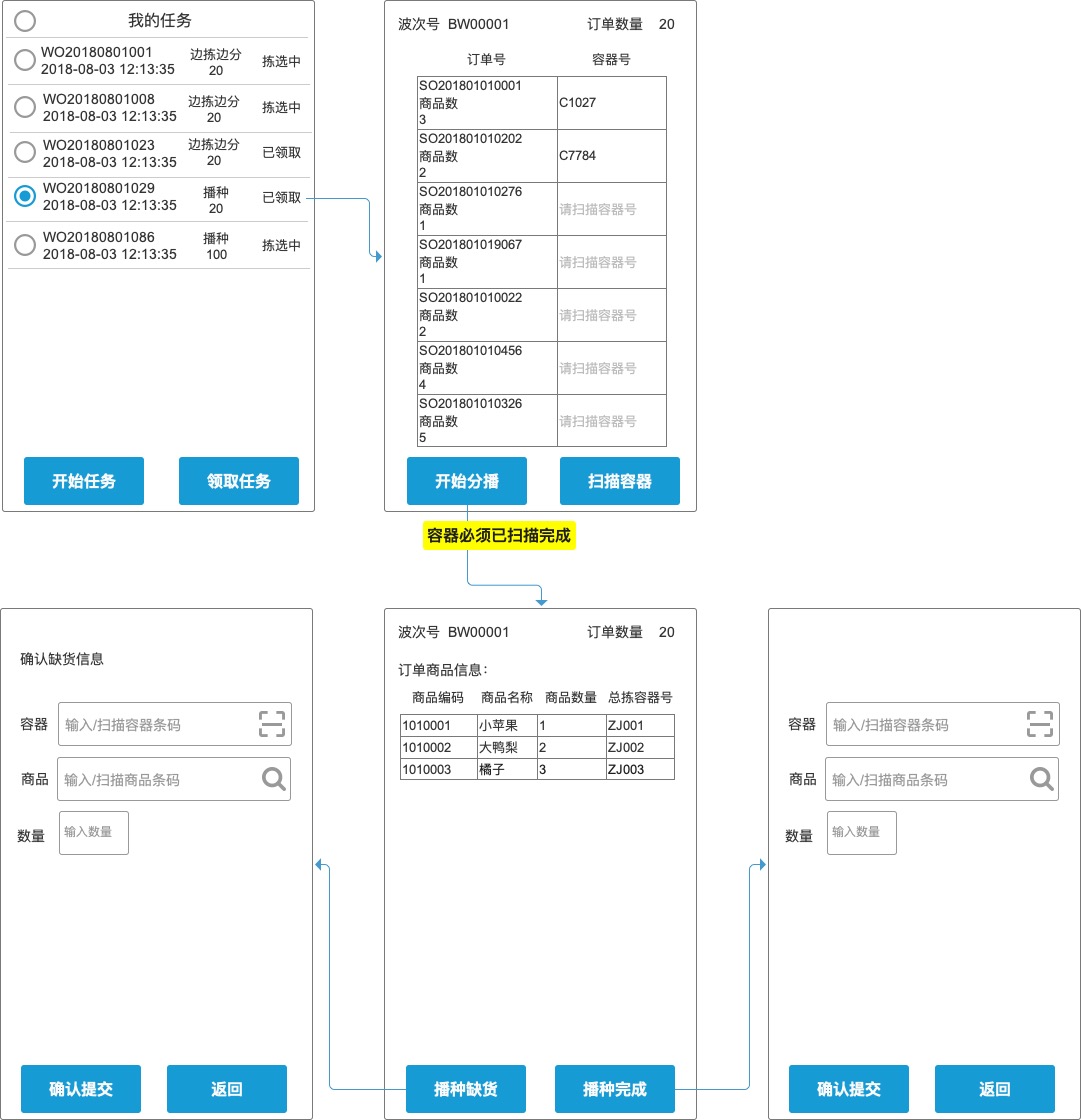
In the process of sorting goods, there will also be the risk of shortage, and there needs to be an entrance for abnormal handling. And what needs to be remembered is that in the design of the system, the end of the picking task cannot be blocked because of abnormal shortage, which will lead to the suspension of the subsequent process. For sowing and picking fruits, the design idea of exception handling is the same.
This paper mainly introduces the common picking methods and picking process design in the warehouse. I hope today’s sharing can help you. Thank you for your attention. PS, I don’t know if you have found one thing. Picking while dividing is actually a combination of picking fruits and sowing, so it is also called compound picking.
Elk Products, WeChat official account: Elk Product Manual, everyone is a product manager columnist. Focus on supply chain mining and upgrading, love life and love products.
This article was originally published in everyone is a product manager. Reprinting is prohibited without permission.
The title map comes from Unsplash and is based on CCO protocol.
关于作者